



What is bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery is a weight loss surgery, where a change in intestinal architecture is done and weight loss occurs gradually over a period of time.
Why bariatric surgery is also called Metabolic surgery?
Obese people may be suffering from diabetes mellitus and other co-morbidities, together called as Metabolic Syndrome.
Bariatric Surgery (though considered as cosmetic surgery) helps treat metabolic syndrome, hence called as metabolic surgery.
What problems are associated with obesity?
Obese patients are either suffering from or at risk of various co-morbidities. These includes:
How do I know I am obese?
Obesity is defined on the basis of Body Mass Index (BMI).
BMI (kg/m2) = {Weight in kilograms ÷ (Height in metres)2}
e.g. a person with weight 70 kgs and height 165 cms, BMI = {70 ÷ (1.65)2} = 25.71 kg/m2
Obesity index | BMI (Western population) | BMI (Asian population) |
Normal | 18.5-24.9 | 18.5-22.4 |
Overweight | 25.0-29.9 | 22.5-27.4 |
Class I Obesity | 30.0-34.9 | 27.5-32.4 |
Class II Obesity | 35.0-39.9 | 32.5-37.4 |
Class III or Morbid Obesity | 40.0-49.9 | 37.5-47.4 |
Super morbid obesity | >50.0 | >47.5 |
Who needs bariatric surgery?
Indications for bariatric surgery are:
BMI >40 kg/m2 with or without co-morbidities (>37.5 for Indian population).
BMI >35 kg/m2 with co-morbidities (>32.5 for Indian population)
In patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus and BMI >32.5 kg/m2 (>30.0 for Indian population), Bariatric (Metabolic) surgery may be considered.
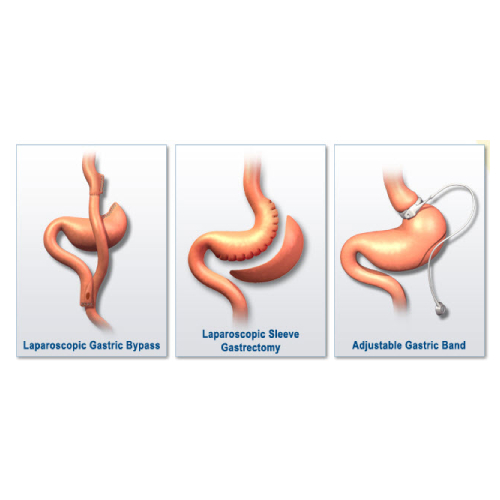
What are the bariatric surgery options available?
There are mainly 2 types of bariatric procedures:
1)- Sleeve Gastrectomy. 2)- Gastric bypass procedures.
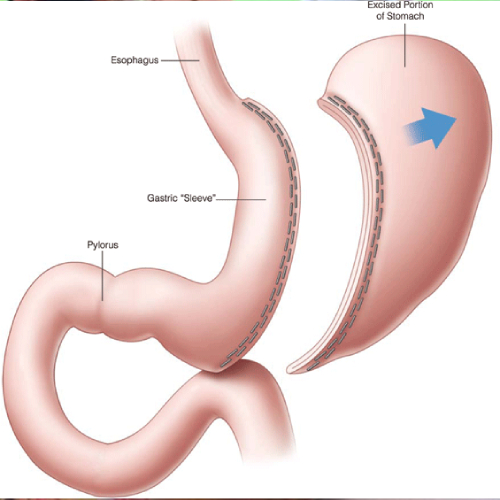
Sleeve gastrectomy: In sleeve gastrectomy, greater wall of stomach is removed using endo-staplers which cuts and seal the stomach, only a small portion of stomach (approximately 60-100 ml) is left behind. Stapled portion of stomach is doubly secured using endo-suturing to prevent leak or bleeding.
Greater wall of stomach produces Ghrelin hormone (hunger hormone) which stimulates appetite, increases food intake and promotes fat storage. Removal of greater wall of stomach in sleeve gastrectomy brings hormonal changes in the body which causes weight loss.
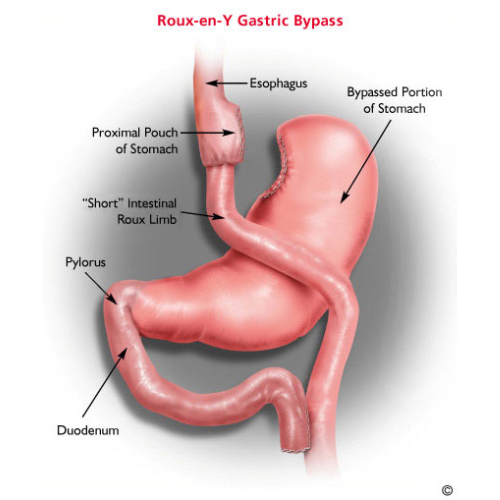
Gastric bypass procedures: Roun-en-Y gastric bypass or mini-gastric bypass are the options available, where connection is created between stomach and small intestine, so that food goes directly into distal intestine, bypassing proximal part of intestine.
Only small portion of food ingested is digested and thus absorbed into the body. It causes malabsorption and major portion of food is excreted out in stools.
Which procedure should I undergo?
It is decided by your surgeon after seeing all your parameters and dietary habits. The best option is selected considering the patient’s safety as priority.
What weight loss can be expected after bariatric surgery?
Approximately 70% of your excess weight is lost in initial 8-10 months. Almost 90% of your excess weight loss occurs in 1.5-2 years.
What complications can occur after bariatric surgery?
While there are risks associated with any kind of operation, most laparoscopic bariatric patients experience a few or no complications in expert hands.
Complications of laparoscopic bariatric surgery are infrequent, but includes bleeding, infection, unintended injury to adjacent structures, staple line leakage, pneumonia, deep vein thrombosis or aggravation of medical conditions.
Gastric bypass procedures can have late complications like bleeding due to stomal ulcers, sudden blood pressure or sugar changes due to dumping syndrome, or intestinal obstruction due to internal hernias.
Patients may require nutrient supplementation after bariatric surgery to prevent nutritional deficiencies.
How is recovery after bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery is performed laparoscopically. Three to five small punctures are made, varying in size from 5-10 mm. Procedure is performed under general anaesthesia (GA).
Patient is ambulated and started on liquid diet four hours after the surgery.
Oral diet is followed according to diet plan under dietician’s guidance.
Patients may have drain pipe attached to their body which will be removed before discharge.
Most of the patients get discharged on second day after the surgery.
No stitches are applied which need to be removed.
Patients will have follow-up 1 week, 1 month, 3 months after the surgery; and 6 monthly thereafter.
What are benefits of laparoscopy surgery?
Early recovery after surgery.
Decreased pain.
Better cosmesis. Minimal scar on the abdomen.
Early return to work.
Better surgical precision could be achieved.
“Laparoscopic bariatric surgery is the only modality which provides sure, effective and permanent weight loss.”
“Advancement in technology and expertise has made bariatric surgery a safer option.”
“It gives obese people an opportunity to attain better, healthier, respectful and active life.”