

What is Gallbladder?
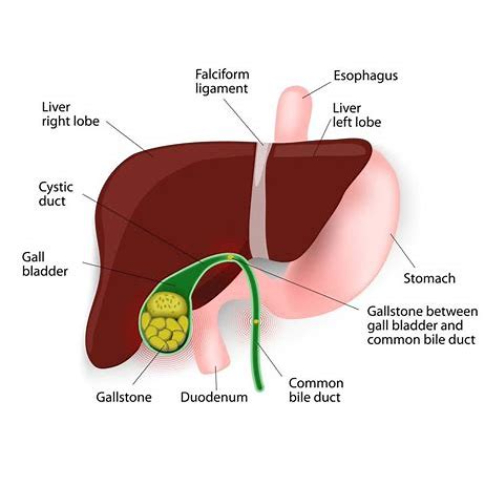
Gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ which rests beneath the Liver. It stores and concentrates a digestive fluid called bile, which is secreted by the liver.
What problems can occur to the Gallbladder?
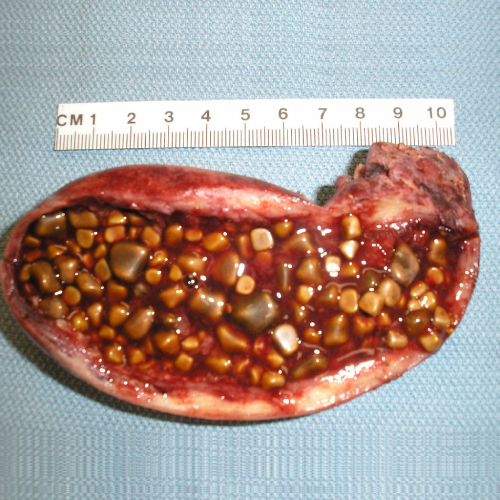
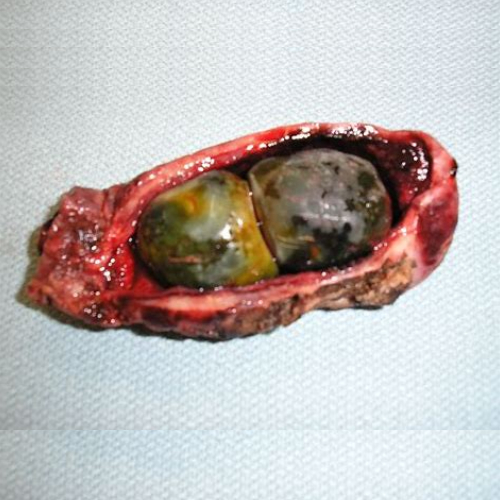
Most of the gallbladder problems are caused due to presence of gallstones (Cholelithiasis).
This can lead to inflammation of the gallbladder (Calculous Cholecystitis).
Some patients (Diabetic, immuno-compromised, old age, taking steroids) can have gallbladder inflammation in absence of gallstones (Acalculous Cholecystitis).
Patients may have Gallbladder Polyp, with or without gallstones, which may require further observation or surgical treatment.
Why Gallstone forms?
Gallstones occur due to complex interaction of genetic and environmental factors.
Increasing age, female sex, obesity, western dietary habits, decreased physical activity, weight loss and certain drugs are associated with its aetiology.
Some diseases, like liver cirrhosis, inflammatory bowel disease, cystic fibrosis and haemolytic diseases, have increased chances of gallstone formation.
Gallbladder stones are especially very common in North Indian population.
What are the symptoms caused by Gallbladder stone?
Most common symptom after gallstone disease is dyspepsia or epigastric discomfort / fullness.
Biliary colic is next common symptom presenting as pain below right costal margin, sometimes radiating to back. Inflamed gallbladder can lead to continuous and increased intensity pain.
Patient may also have nausea, vomiting, fever or jaundice due to gallstones.
How is Gallbladder disease detected and treated?
Abdominal Ultrasonography (USG) is the investigation of choice to diagnose gallbladder pathology. Sometimes, advanced investigations like MRCP, EUS or CT scan may be required in difficult situations.
Gallstones do not go away of its own, but can be temporarily managed with drugs or dietary adjustments.
Symptoms will eventually continue unless the gallbladder is removed.
Why Gallbladder stone needs surgery?
No effective medical treatment is available to dissolve gallstones.
Surgical removal of the gallbladder is the time honoured and the safest treatment of gallstone disease.
Further, gallstones if untreated, can lead to complications.
What changes can occur after Gallbladder removal?
Approximately 1-1.5 litres of bile is produced by liver, and only 30-50 ml is stored in gallbladder. After gallbladder removal, common bile duct gradually dilates, and bile directly drains through common bile duct into the intestines.
Removal of the gall bladder is not associated with any impairment of digestion in most people as the diseased gallbladder has already lost its functional capacity.
What preparation is required for Gallstone removal surgery?
Preoperative preparation includes blood test, medical evaluation, chest x-ray and an ECG depending on the age & medical condition.
After midnight the night before the operation, you should not eat or drink anything except medications that your surgeon/anaesthetist has told.
Drugs such as aspirin, blood thinners, anti-inflammatory medications & vitamin E need to be readjusted temporarily for several days prior to surgery.
How is Gallbladder removal surgery performed?
Laparoscopy Cholecystectomy is the gold standard treatment for gallbladder removal. Also called as ‘doorbeen’ or ‘laser’ surgery by common people.
Performed under General Anaesthesia (GA).
Usually three to four small punctures are made in the abdomen, approx. 5-10 mm in size.
A telescope is passed into one of the punctures to see inside the abdomen.
Using laparoscopic instruments, surgery is performed and gall bladder is removed.
Usually skin is closed with absorbable sutures and need not be removed later.
A drain may be placed during the procedure in difficult situations, which would be removed after 24-48 hours.
What are benefits of laparoscopy surgery?
Early recovery after surgery. Many people can be treated as day-care procedure where they can be discharged on the same day, or next day morning.
Decreased pain.
Better cosmesis. Minimal scar on the abdomen.
Early return to work.
No residual weakness.
Better surgical precision could be achieved.
What if operation cannot be performed by the laparoscopic method?
In a small number of patients, the laparoscopic method cannot be performed.
If the surgeon feels that it is safer to convert the laparoscopic procedure to open one, it is not a complication, but rather sound surgical judgment.
The decision to convert to an open surgery is strictly based on patient’s safety.
What complications can occur?
While there are risks associated with any kind of operation, most laparoscopic gallbladder patients experience a few or no complications and quickly return to normal activities.
Complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy are infrequent, but includes bleeding, infection, unintended injury to adjacent structures which may require another surgical procedure to repair it, bile leakage, and escape of stones into the common duct or abdominal cavity, pneumonia or aggravation of medical conditions.
Is laparoscopy risky for people with other medical problems like Diabetes, Hypertension, Kidney disease or Morbid Obesity?
Not at all. On the contrary, minimization of the trauma to the body by Minimal Access Surgery (MAS) causes minimal disturbance of normal physiology.
Can laparoscopy be performed in children?
Yes, laparoscopic removal of gallstones can be safely performed in paediatric population as well.